Auger Electron Spectroscopy (AES)
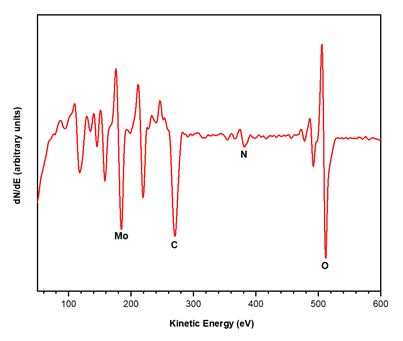
Auger electron spectroscopy (AES) is a surface-sensitive analytical technique with high lateral resolution. It is used to quantify and map the elemental composition of the outermost 2-10 nm of a material.
Strengths
- Very high lateral resolution (as small as 5 nm)
- Provides quantitative elemental composition and chemical state identification
- Acute surface selectivity (typical information depth is ~ 3 to 10 nm)
- Excellent for elemental mapping
Limitations
- Reproducibility can vary
- Charging affects different portions of the spectra by different amounts, which can make analysis difficult
- Analysis is destructive

