Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
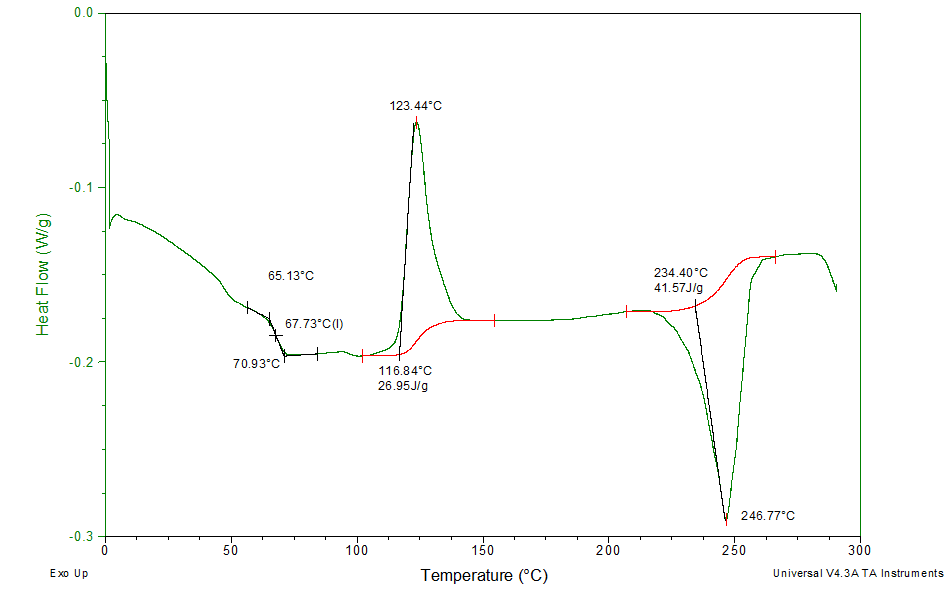
Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) is a thermal analysis technique used to characterize a variety of temperature-dependent physical and chemical changes in a material.
Strengths
- Direct method of measuring heat capacity and detecting thermal transitions in the material
- Straightforward data collection
- 3 sample pan types available to accomodate different material types
Limitations
- Oxidation analysis, volatile material characterization, thermal degradation experiments, and solvent loss measurements are not supported as they can permanently damage the instrument
- Upper temperature limit must be lower than material decomposition temperature

