Electron Probe Microanalysis (EPMA)
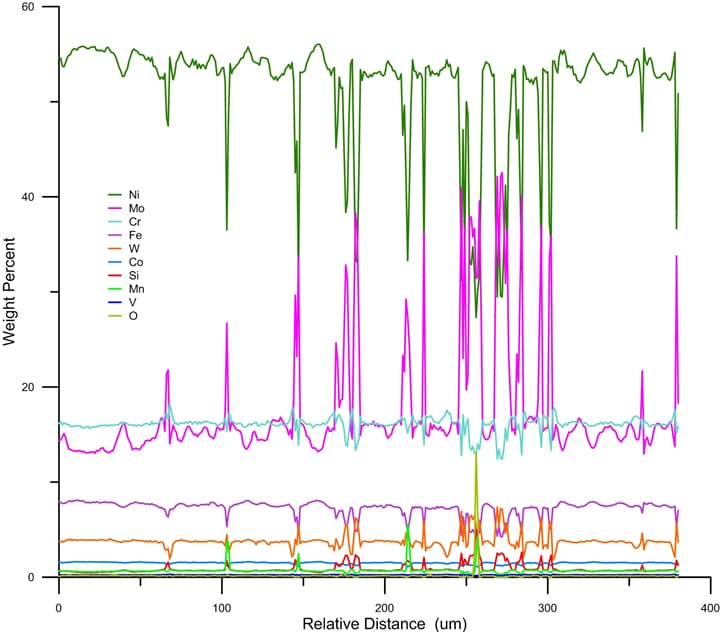
Electron probe microanlysis (EPMA) is a non-destructive technique used for high-sensitivity, quantitative determination of the elemental composition of a material.
Strengths
- Quantitative elemental analysis down to within ~10 to 100 ppm sensitivity
- Simultaneous data collection of up to 5 element signals
- Highest lateral resolution among elemental microanalysis techniques
- Elemental mapping enabled
Limitations
- Measurements are time-intensive compared to energy dispersive x-ray spectroscopy (EDS or EDX)
- For quantitative results, elements must be calibrated against standards
- Light elements (Be through N) can be difficult to measure accurately
- Spatial resolution limited to ~ 1 µm


