X-ray Absorbance Spectroscopy (XAS)
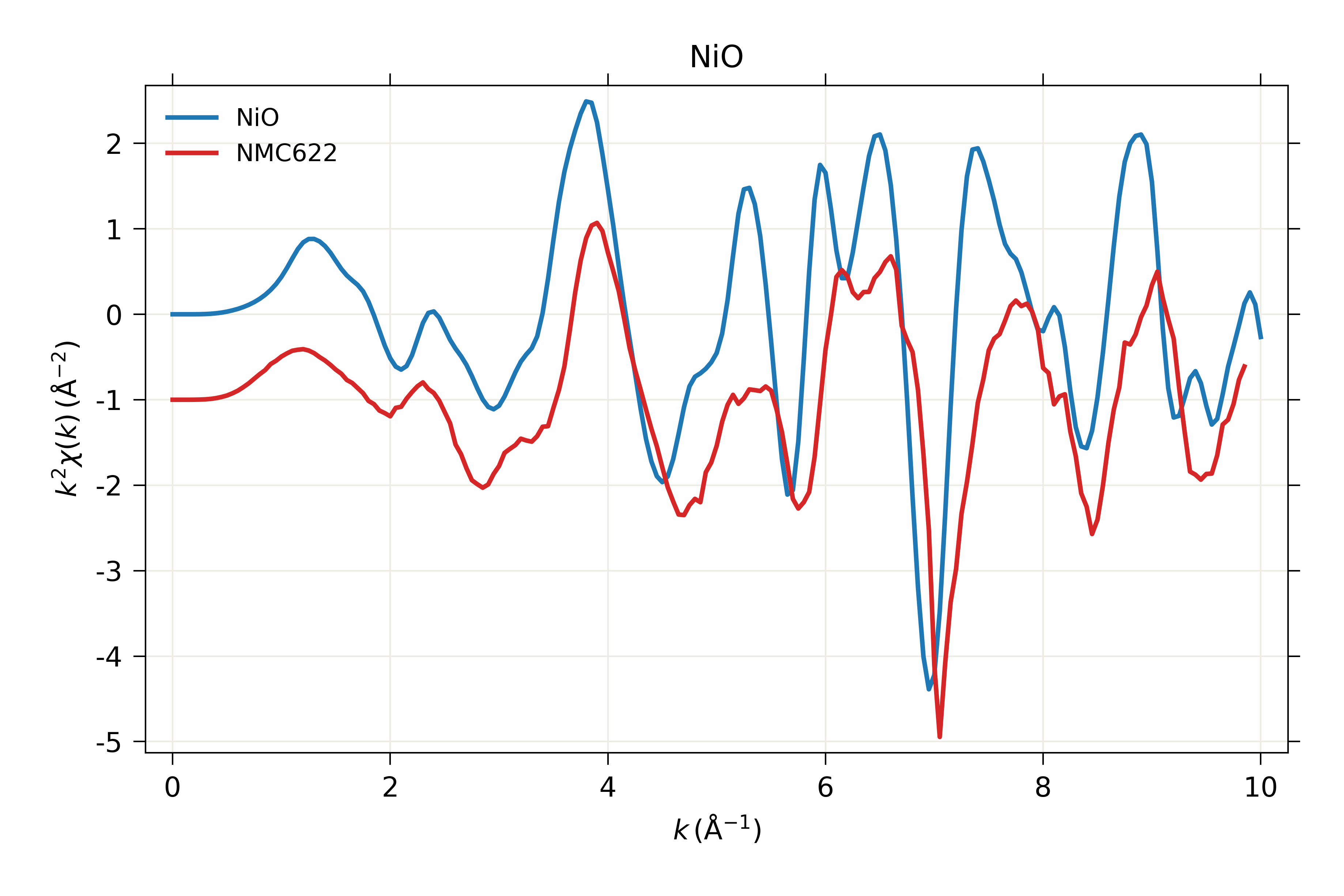
X-ray absorption spectroscopy is a technique used to analyze the electronic structure of atoms and molecules by measuring the energy absorption of X-rays as they interact with a sample, providing insights into its chemical composition and bonding.
Strengths
- X-ray absorption spectroscopy is element-specific, enabling analysis of specific elements within a sample, even in complex mixtures.
- XAS provides valuable structural and chemical information about the local environment of the absorbing atom, such as coordination number, bond distances, and oxidation state.
- Easy sample preparation and bulk sensitive, not limited to sample surfaces.
- Can perform in situ and in operando measurements, for example during battery cycling.
- Does not require long range structural order.
Limitations
- Limited spatial resolution: X-ray absorption spectroscopy typically provides information on the average properties of a sample, and its spatial resolution is often limited, making it challenging to study fine-scale variations in a sample.
- Samples must be sufficiently concentrated to measure.





