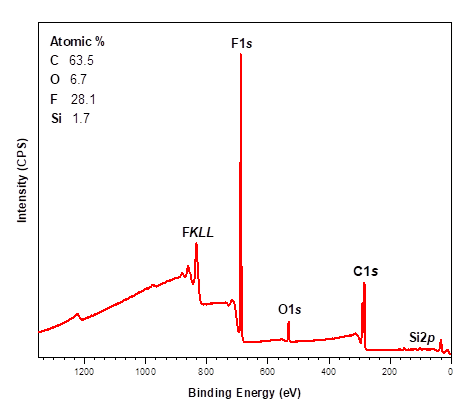
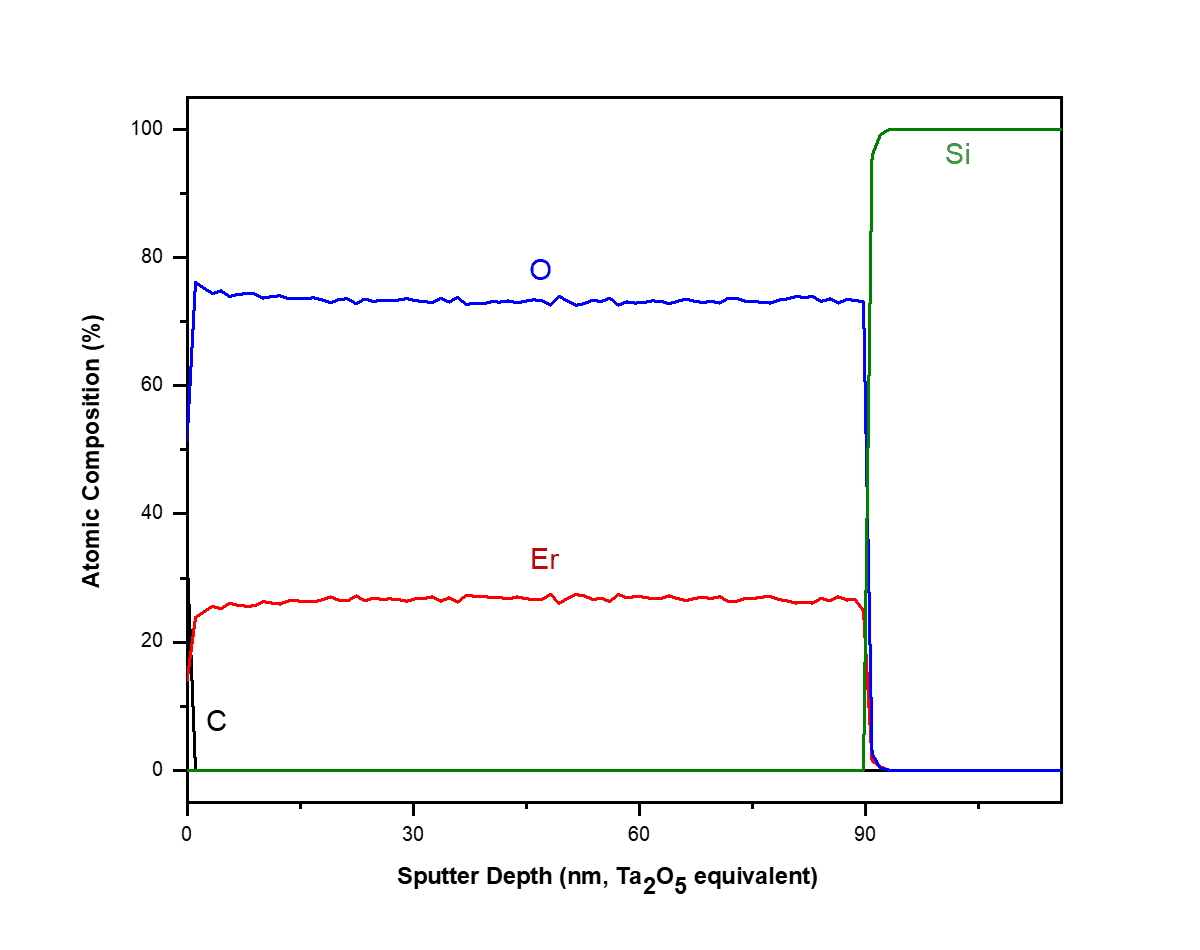
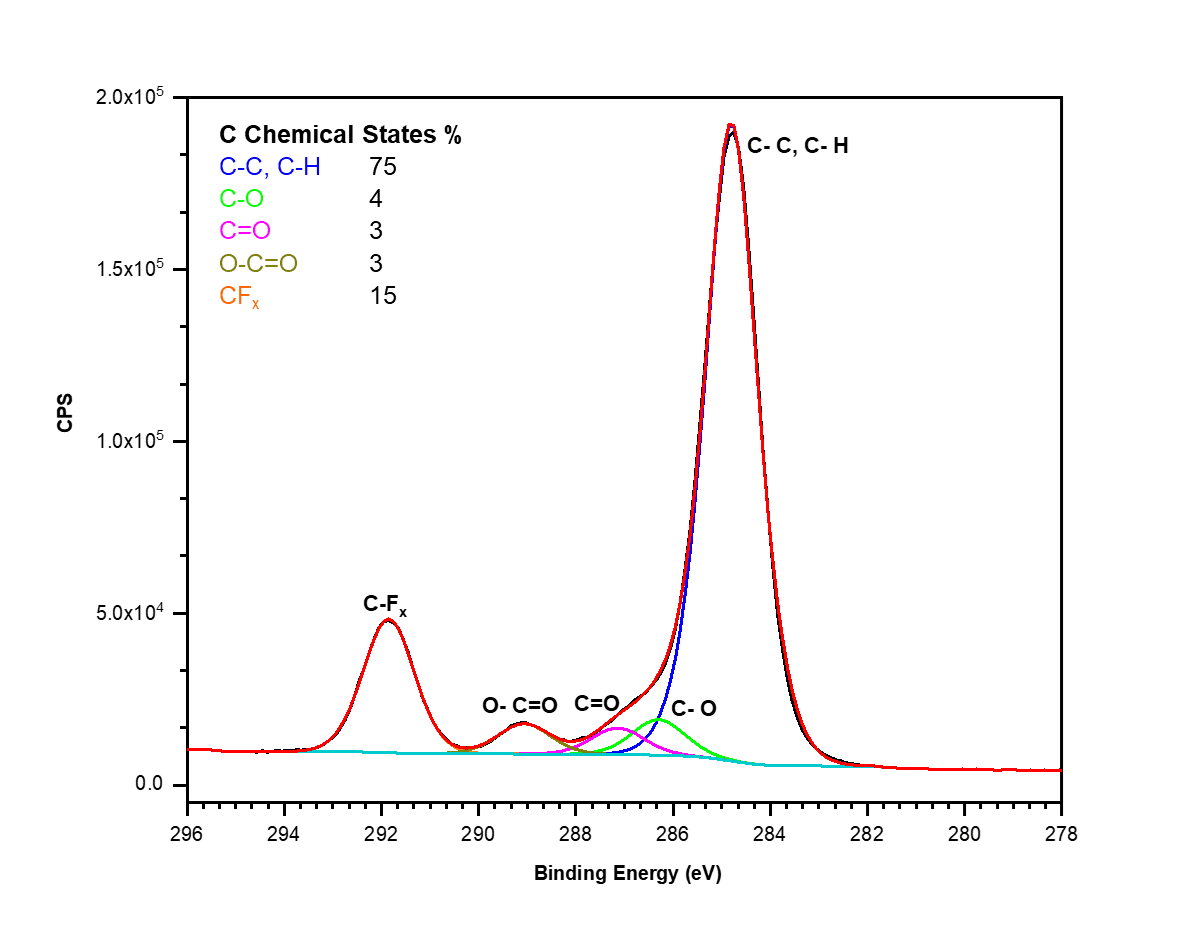
X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS)
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) is a highly surface-specific chemical analytical technique used to probe the elemental composition and bonding states in the outermost 2-10 nm of a solid surface.
Strengths
- Quick and easy sample preparation
- Rapid data acquisition
- Accurate quantitative elemental composition in the near-surface region (2-10 nm)
- Charge neutralization is possible for non-conducting materials
Limitations
- Lateral resolution limited to about 10 microns
- Sputter depth profiling to assay chemical changes with depth can lead to artifacts and sample damage
- Bonding information cannot always be determined