Dynamic Mechanical Analysis (DMA)
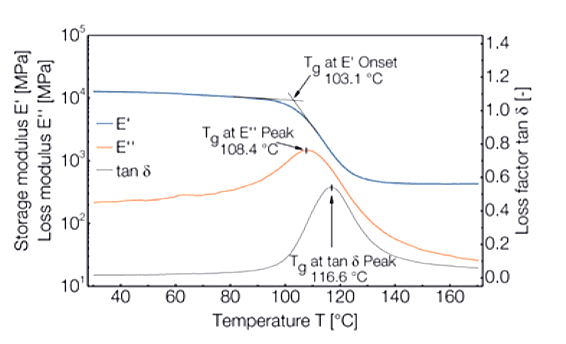
Dynamical mechanical analysis (DMA) is used to study changes in the mechanical properties of a material under periodic stress as the temperature is varied. DMA results are used to assess: glass transitions, melting points, elastic modulus, strain-to-break, toughness, creep, and numerous other thermal and mechanical properties.
Strengths
- Ultra-high sensitivity to deformation and displacement
- Improved detection threshold for thermal transitions (vs. Differential Scanning Calorimetry)
- High flexibility in experiment design
- Rapid and straightforward data collection
- Particularly well-suited for high-stiffness polymers
Limitations
- Data quality is impaired by rough, asymmetric, and irregularly-shaped samples
- Analysis is destructive


